Has a sultry beach vacation ever left reddish or light brown circular spots on your face? There are high chances that these are harmless freckles, which usually develop on fair skin after constant sun exposure.
Some women feel freckles add to their beauty, while others want to get rid of them. In this post, we will tell you how to differentiate between freckles and other dark spots on the face and body. We will also cover various treatment options for freckles.
Highlights:
1. What Are Freckles?
Freckles are harmless clusters of tiny brown or reddish spots on the skin caused due to sun exposure. They are about 1 - 2 mm in size and usually appear on the face, neck, arms, back and chest. In most cases, they fade away during the winter months. People with a fair complexion, red hair and green eyes are more prone to freckles. [1]
2. What Causes Freckles?
A. Sun Exposure
Freckles, also called ephelides, are caused due to prolonged exposure to the sun, which leads to a spike in melanin (brown skin pigment) and melanocytes (melanin cells).
B. Role Of Genetics
Freckles in some people can be hereditary. The human body can produce two types of melanin - Eumelanin and Pheomelanin. The type of melanin that your body produces depends on a major freckle gene called MC1R [2].
Eumelanin protects the skin from harmful UV rays and is produced in people with dark skin, hair and eyes. Pheomelanin is produced in people with lighter skin, hair and eyes.
3. Difference Between Freckles, Lentigines (Age Spots Or Sun Spots) And Moles
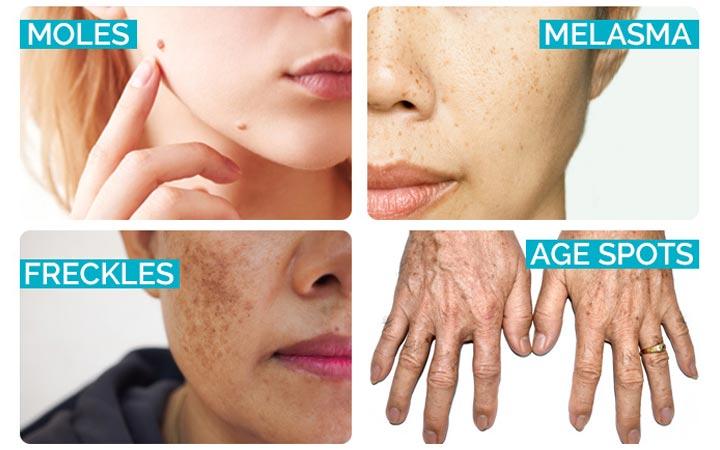
Freckles are often confused with other pigmented spots. They differ from solar lentigines (age spots or sun spots) [3] and Melanocytic Nevus [4] (moles or birthmarks) in appearance as well as longevity. Take a look at the image and table below to understand the difference:
|
|
Freckles |
Lentigines, age spots or sun spots |
Moles |
|
Structure |
Multiple, tiny brown, flat spots |
Larger and defined brown spots |
Flat to slightly bumped brown spots |
|
Cause |
Sun exposure and genetics |
Sun exposure |
Skin cells grow in cluster |
|
Size |
1-2 mm |
Less than 6 mm |
2mm or more |
|
Age group |
Can appear in children and adults |
Appear in elderly people |
Present from birth or can develop in teenage |
|
Who is prone? |
Light skinned people are prone to freckles |
People with any skin color can develop |
People with any skin color can develop |
|
Seasonal changes |
Usually fade away in winter |
Usually remain the same |
Can remain or disappear |
4. Treatment For Freckles
Freckles are usually harmless and do not need medical intervention. But a variety of treatments are available to lighten their appearance. However, freckles reappear due to sun exposure. Skincare experts believe that regular sunscreen application goes a long way in preventing freckles.
Consult a certified dermatologist and consider one of these methods or combination therapies to treat freckles:
A. Bleaching Creams
Use a topical bleaching cream or fading cream containing ingredients like kojic acid or hydroquinone (in a concentration of 2%). When used over time, they have the capacity to lighten freckles.
Note:
Always perform a patch test before applying on your face directly as they may cause burning or dryness.
B. Retinoids
Retinoids [5] are vitamin A derivatives that have skin lightening power. They function by absorbing harmful UV-B radiation. Side effects of retinoids include redness, irritation and sensitivity.
C. Cryosurgery
This is an in-office treatment that involves freezing the freckles with liquid nitrogen. Cryosurgery is safe and seldom causes scarring. However, it may cause bleeding or hypo-pigmentation [6].
D. Laser
Laser treatment or light therapy [7] involves the use of light to target freckled skin. It is effective at getting rid of freckles but can cause side effects like redness or itchiness. Consult your dermatologist before starting a session.
E. Chemical Peels
Chemical peels [8] rely on chemicals like glycolic acid or lactic acid to exfoliate the skin. Top layer of the darkened skin is removed so that a new and fresh layer pushes up. There may be temporary stinging and redness that fade away.
F. Sunscreen
Sunscreen cannot treat the existing freckles but can prevent its further development. The best sunscreens are the ones with SPF 30 or higher. Use it at all times during the year. Apply it 20 minutes before going outdoors and reapply every two hours.
G. Home Remedies
Home remedies may not be as effective as other treatments. However, people have been using them to minimize pigmentation. None of them are scientifically proven, but here are a couple of remedies you can try:
1. Lemon
Lemon juice contains Vitamin C or ascorbic acid that is an excellent skin lightening agent.
2. Honey
Honey contains flavonoids that inhibit tyrosinase [9] activity and reduce the appearance of freckles.
3. Yogurt
Yogurt contains lactic acid which works like a tyrosinase inhibitor.
4. Aloe Vera
Aloe Vera inhibits the tyrosinase activity, thereby reducing the production of melanin.
5. How To Prevent Freckles?
- Use a sunscreen with SPF (sun protection factor) 30 or above
- Reapply sunscreen every 2 hours while you are out in the sun
- Avoid stepping out when the sun’s rays are at their peak (10 am to 4 pm)
- Wear sun-protective clothing and hats
6. Makeup Tips For People With Freckles
- Start with cleansing and moisturizing.
- Pick a sheer foundation as anything opaque can make the freckles look muddy.
- Choose products that match your skin undertone.
- Conceal your freckles with a good concealer.
7. Can People Of Any Race Have Freckles, Or Is It Just White People?
Although freckles are most common in skin types 1 and 2 of the Fitzpatrick scale, it can be found in all ethnicities.
What Is The Fitzpatrick Scale?
The Fitzpatrick scale [10] or the Fitzpatrick skin type test is a classification for human skin color, developed by Thomas Fitzpatrick in 1975.
- Type 1 - It never tans but always burns
- Type 2 - It tans to an extent and usually burns
- Type 3 - Tans uniformly and burns mildly
- Type 4 - Tans to moderate brown and burns minimally
- Type 5 - Easily tans (dark brown) and rarely burns
- Type 6 - Tans heavily and never burns

8. When To See A Doctor?
Freckles are harmless in most cases. People with freckles are sensitive to the sun. So it is important to protect your skin while stepping outdoors. Consult a dermatologist if a freckle:
- Bleeds
- Itches
- Changes in size, shape or color
1. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5103577/
2.https://medlineplus.gov/genetics/gene/mc1r/
3. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24517859
4. https://www.aocd.org/page/Retinoidstopical/
5. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2186791
6. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5605211/
7. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3560166/
8. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20682135
9. https://healthywa.wa.gov.au/Articles/S_T/Types-of-skin-cancer
Recommended Products
Was this Article helpful?
- Least helpful
- Most helpful











