You spend years perfecting your skin and suddenly you have a skin infection! How do you deal with it? If it makes you confused and clueless, we are here to give you all the answers. Keep reading to know about common skin infections, their symptoms and treatment methods.
Highlights:
- What Are Skin Infections?
- How Does A Skin Infection Start?
- Different Types Of Skin Infections & Their Treatments
- How Do You Prevent Skin Infections
- How Are Skin Infections Diagnosed?
- How Do You Know When A Skin Infection Is Serious?
- Can A Skin Infection Go Away On Its Own?
- Can Your Body Fight Skin Infection Without Antibiotics?
What Are Skin Infections?
Skin infections occur when your skin is invaded by a foreign microorganism like bacteria, fungi, virus or parasite [1]. They can be mild or serious, with the latter requiring medical attention.
How Does A Skin Infection Start?
The outermost layer of the skin (stratum corneum) forms a protective barrier and prevents harmful microorganisms like bacteria and fungi from entering the skin. When the skin barrier is damaged, your skin is prone to skin infections.
Physical aggressors like sunlight, smoking, extreme temperatures and wrong skin care products can damage the skin barrier. A cut or a wound can also pave way to infections in the skin [2]. Deeper the infection penetrates, severe the condition.
Different Types Of Skin Infections & Their Treatments
1. Bacterial Skin Infections
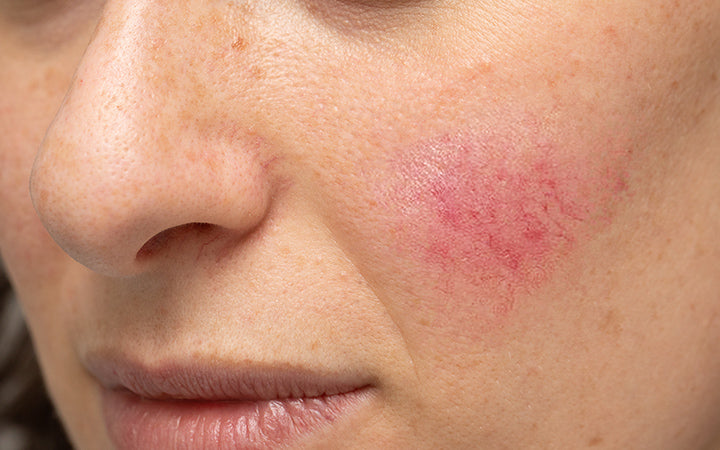
Causes
Bacteria like staphylococcus or streptococcus can enter via a cut or injury on the skin. Weakened immune system makes it easier for the bacteria to enter your skin.
Common bacterial skin infections include cellulitis, impetigo, boils and leprosy. [3]
Treatments
Bacterial infections are treated with topical or oral antibiotics. Severe forms of infections may need intravenous administration of antibiotics.
|
Name of infection |
Cellulitis |
Impetigo |
Boils (Staph) |
|
Symptoms |
Pain, swelling, tenderness |
Pus-filled blisters or pustules |
Blistered and peeled skin. Fever and chills |
|
Site of appearance |
Near skin ulcers or wounds |
Face, arms, or legs |
Under arms and around the groin |
|
How long will it take to cure? |
7-10 days |
2 -3 weeks |
About 10 days/span> |
|
Severity |
Affects deeper layers and can become serious and life threatening |
Usually not serious |
Usually not serious |
|
Moisturization |
Less hydrating and moisturizing |
More hydrating and moisturizing |
More hydrating and moisturizing |
|
Who gets it |
Common in middle aged and elderly |
Common in children |
Infants and children under 6 |
|
Risk factors |
Injury, cut, burn, weakened immune system, obesity |
Crowded places, warm and humid climate |
Diabetes, weakened immunity, contact from a person with boils |
2. Viral Skin Infections

Causes
Viral skin infections are caused by viruses, which are microbes that can multiply only when it is inside a living organism like a human being. Herpes virus, human papillomavirus (HPV) and pox virus groups are the common virus groups that infect the skin. The most common viral skin infections are shingles, chicken pox, warts,measles and hand, foot and mouth disease.[4]
Treatments
Anti-viral treatments are used for viral skin infections. In some cases, your dermatologist may remove the skin growth.
|
Name of infection |
Warts |
Herpes |
Hand, foot, and mouth disease |
|
Symptoms |
Small bumps, rough to touch |
Blisters, ulcers, cold sores |
Blister, peeling, rashes, or red spots |
|
Site of appearance |
Hand, feet |
Mouth, groin |
Palms, soles of feet and around mouth |
|
How long will it take to cure? |
6 months to 2 years |
2 - 3 weeks |
7 - 10 days |
|
Severity |
Not severe but contagious |
Not usually serious |
Not usually serious |
|
Who gets it |
Any age but common in school children |
14-49 age group |
Infants and upto 5 years old |
|
Risk factors |
Skin injuries |
Smoking, alcohol, exposure to sun |
Contact from other children |
3. Fungal Skin Infections

Causes
They are caused by microbes called fungi, which feed on organic matter. Warm and moist surfaces breed fungal infections, which means wearing sweaty clothes or maintaining poor hygiene can lead to the condition. Athletes foot, yeast infection, ringworm, nail fungus, oral thrush and diaper rash are some of the common skin infections caused by fungi. [5]
Treatments
Antifungal creams, gels, sprays are used to treat fungal skin infections. Look for ingredients like zinc, coconut oil, neem oil and tea tree oil. Oral medication like fluconazole may be prescribed in case the infection has not subsided with topical medications.
|
Name of infection |
Athlete’s foot |
Ringworm |
Yeast infections |
|
Symptoms |
Itching and burning between the toes, cracked and dry skin |
Fissures, peeling, red rashes, or scaly patches |
Rash, itching, patches that ooze fluid |
|
Site of appearance |
Feet |
Feet, groin |
Arm pits, groin |
|
How long will it take to cure? |
1 - 4 weeks |
2 - 4 weeks |
1 - 2 weeks |
|
Severity |
Severe and can leave open sores |
Usually not serious |
Can turn serious |
|
Who gets it |
15-40 years |
Common in school children |
Common in young women |
|
Risk factors |
Warm and moist environment, infected persons. |
Warm climate, skin to skin contact |
Antibiotics, diabetes, birth control, pregnancy and a weakened immune system |
4. Parasitic Skin Infection

Causes
Parasitic skin infections are caused by parasites, which are organisms that require a host (human skin in this case) for nutrition. When tiny organisms or insects like lice, bedbugs, scabies live on your skin and lay eggs, it can cause parasitic infections. [6]
|
Name of infection |
Lice |
Scabies |
|
Symptoms |
Itching |
Rash and itching |
|
Site of appearance |
Head |
Wrist, elbow, armpits, buttocks |
|
How long will it take to cure? |
2 weeks |
4 weeks |
|
Severity |
Not serious |
Not serious |
|
Who gets it |
Common in school children |
Anyone can get scabies |
|
Risk factors |
Head to head contact with infected persons |
Crowded environments, weakened immune system |
How Do You Prevent Skin Infections?
1. Hand Hygiene
Maintain hygiene by washing your hands often [7]. Clean hands prevent the transfer of germs or bacteria to the face and other parts of the body.
2. Shower After A Workout
Make sure you get rid of the sweat from a work out session with a nice warm shower.
3. Keep Any Wounds Or Cuts Clean
Either cover the cuts with a bandaid or get regular dressings done.
4. Wear Breathable Fabrics
Tight clothes and synthetic fabrics breed the growth of germs. Wear light, loose-fitting and breathable fabrics.
5. Do Not Scratch Itches
It may be tempting to scratch an infection or an insect bite. Refrain from doing so as it may worsen the condition.
6. Vaccinations
Consider vaccination for diseases like chickenpox, shingles, measles and human papillomavirus.
How Are Skin Infections Diagnosed?
Skin infections are usually diagnosed with a physical examination [8]. Your dermatologist will assess the site of infection and appearance. Other types of skin tests include:
1. Biopsy
Biopsy is done by testing a part of skin tissue that is surgically removed. It is then examined to check for malignancy (cancer causing).
2. Patch Test
Allergens that may be responsible for a person’s skin allergy are applied on a part of the skin. Adhesive patches of identified allergens are left for a period of time. Skin is observed for any reaction.
3. Skin Culture
Skin scraping is done to test for the presence of bacteria, fungi or virus.
How Do You Know When A Skin Infection Is Serious?
Skin infection is characterized by symptoms like swelling, pain, blisters, pus from a cut, fever etc. An infection can be considered serious and requires medical attention when there is high fever, extreme pain and swelling that spreads.
Can A Skin Infection Go Away On Its Own?
Most skin infections go away over time, but some of them can infect blood, lungs or other parts of the body. Topical or oral antibiotics are used to cure skin infections. Severe forms of infections might require medical attention.
Can Your Body Fight Skin Infection Without Antibiotics?
Your body’s immune system fights off many kinds of bacteria with its white blood cells. These form a defense system against a lot of microbes. But when the immune system is weakened, it is prone to infections and requires antibiotics.
Antibiotics are medicines that either destroy bacteria or slow down the growth. Antibiotics should be used sparingly as the body may become resistant to antibiotics after a point.
1. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK8301/
2. https://medlineplus.gov/skininfections.html
3. https://medlineplus.gov/skininfections.html
4. https://medlineplus.gov/skininfections.html/
5. https://medlineplus.gov/skininfections.html
6. https://medlineplus.gov/skininfections.html
7.https://www.health.ny.gov/diseases/communicable/athletic_skin_infections/hand_washing.htm
8.https://www.health.ny.gov/diseases/communicable/athletic_skin_infections/hand_washing.htm
Recommended Products
Was this Article helpful?
- Least helpful
- Most helpful











